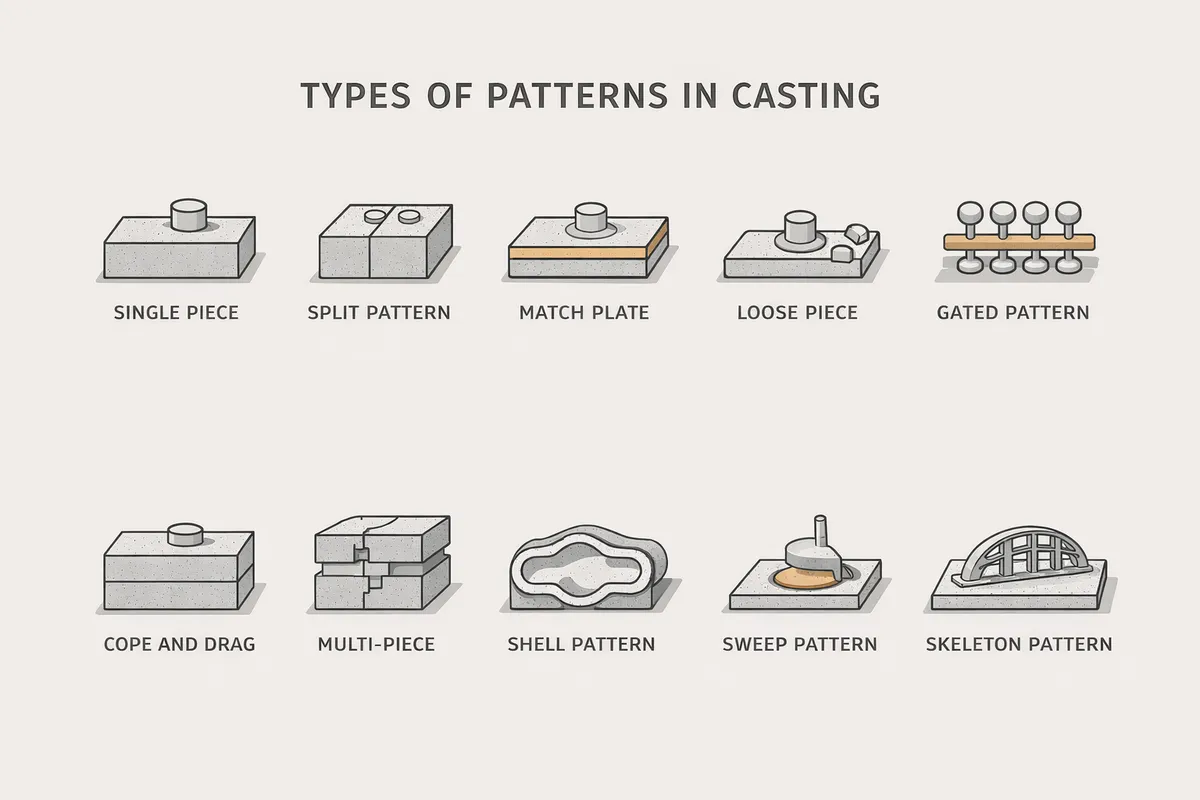
Introduction

Casting stands as a fundamental pillar of modern manufacturing. This ancient yet versatile process, which involves shaping liquid material by pouring it into a mold, is responsible for creating everything from intricate engine components to durable machine parts. It offers unparalleled design freedom and production efficiency. Understanding the core principles of casting is a crucial skill for engineers and designers alike. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the key aspects of the casting process, from the materials and methods used to essential design considerations.
Part I: The Primary Casting Methods
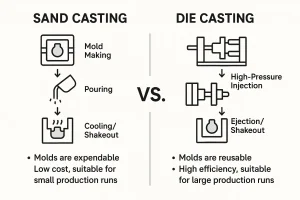
The choice of casting method is a foundational decision that impacts everything from production cost to final product quality. While the underlying principle of pouring molten metal remains constant, the execution varies significantly. For instance, sand casting is a widely-used and cost-effective method where a part is formed using a sand-based mold. This process is ideal for producing large or complex parts and is known for its versatility. In contrast, die casting is a highly efficient method that forces molten metal into a reusable steel mold under high pressure.
When faced with a choice between these two, it is crucial to understand the differences. For a detailed breakdown of the pros and cons, our article on sand vs. die casting provides a thorough comparison.
Part II: Understanding Casting Materials
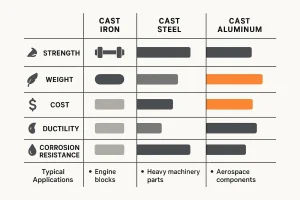
The material you choose has a significant impact on a part’s strength, weight, and overall performance. Each material category offers unique properties that make it suitable for different applications. A popular and durable choice is cast iron, known for its excellent castability and low cost. Within this family, you will find variations like gray iron and ductile iron, each with distinct properties. A common alternative is cast steel, which offers superior toughness and ductility. For a side-by-side comparison, explore our guide on cast iron vs. cast steel.
For lightweight applications where corrosion resistance is a priority, aluminum casting is an ideal solution. When working with this material, it is essential to understand dimensional tolerances and the specific tolerance guide.
Part III: Process and Design Considerations
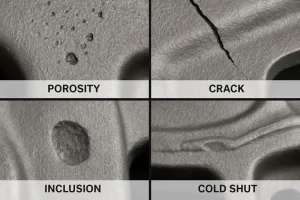
Successfully designing and producing a cast part requires careful attention to many factors beyond the material and method alone. Even a well-executed plan can face challenges, and identifying common casting defects is a vital skill. For example, our guide on gas defects provides detailed insights into a frequent issue.
Furthermore, factors such as casting costs and the use of heat treatment for modifying a part’s properties are crucial for optimizing production. Our articles on post-casting heat treatment and other related topics can provide further guidance.
Conclusion
Casting is a powerful manufacturing process that offers immense design freedom and production efficiency. By mastering the fundamentals and understanding the nuances of different methods, materials, and process details, you can successfully bring complex designs to life. Use this guide as your starting point to explore our full library of casting knowledge and find the information you need.