🧱 Introduction
Aluminum casting plays a pivotal role in modern manufacturing. From lightweight car components to complex aerospace structures, this process transforms molten aluminum into durable, high-performance parts. Its popularity stems from aluminum’s unique balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility—making it ideal for a wide range of industries.

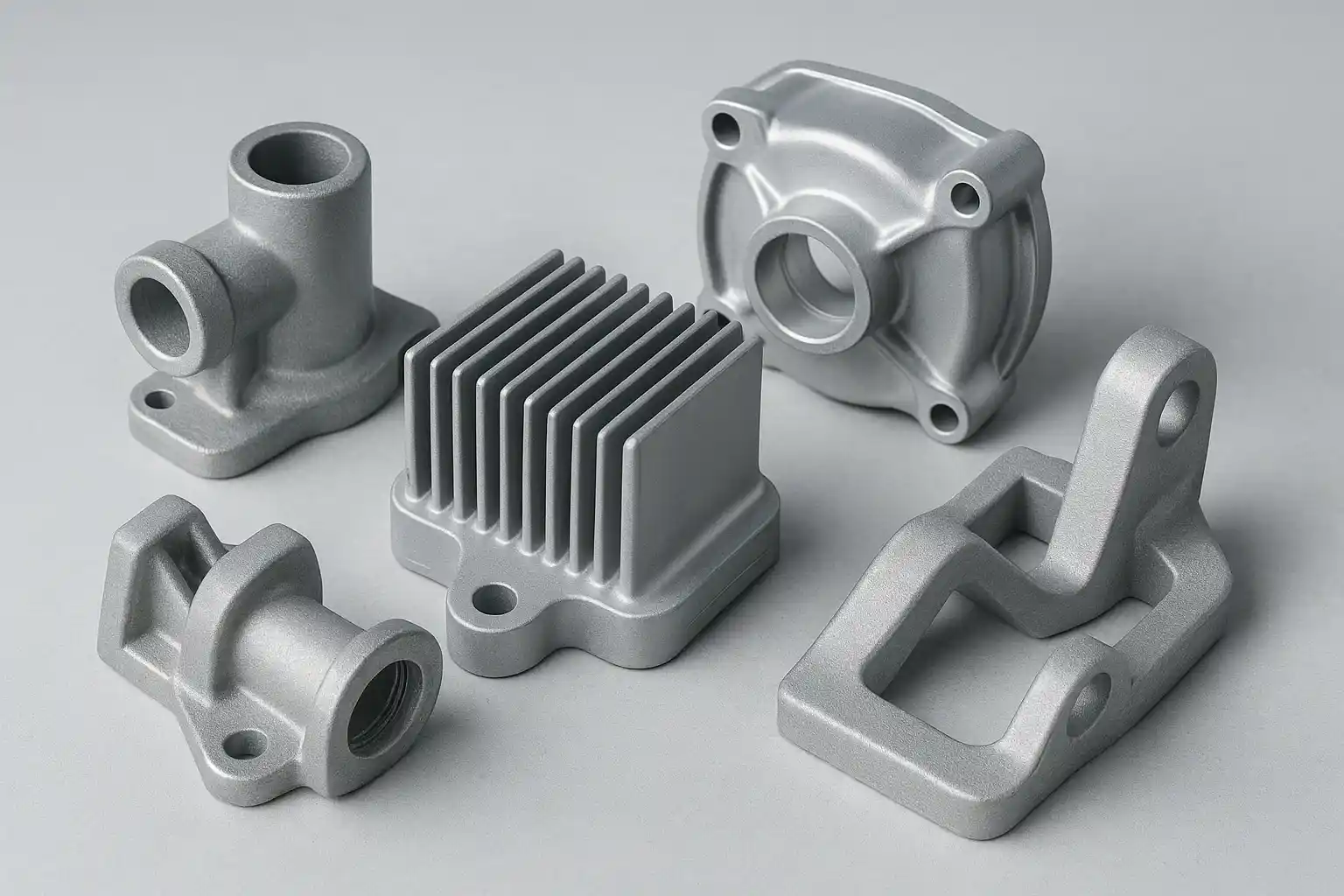
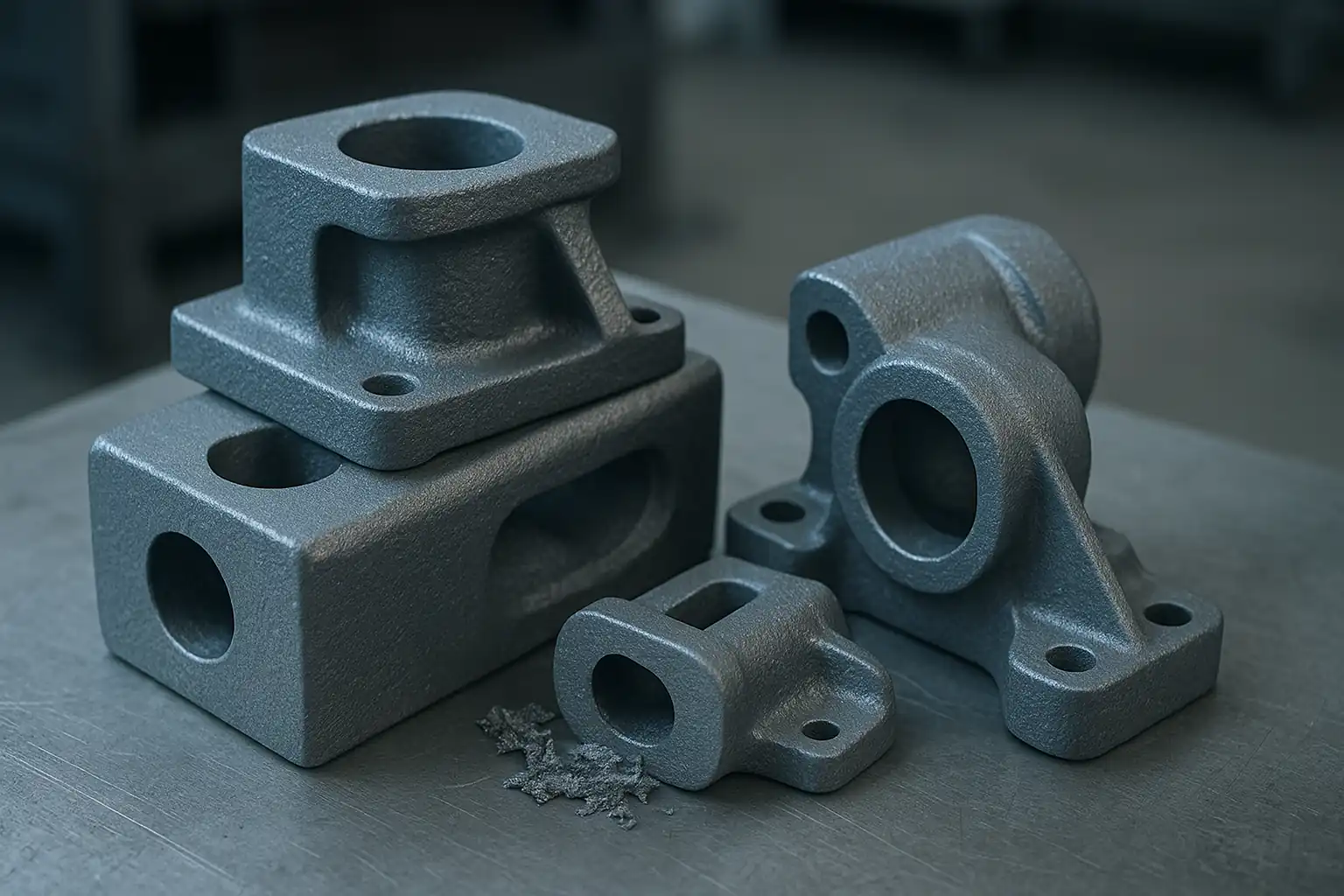
Key aluminum cast parts such as brackets and housings used in automotive and industrial applications
🔍 Understanding Aluminum Casting & Its Value
Aluminum casting refers to the process of shaping molten aluminum into a solid component by pouring or injecting it into molds. It is especially valued for:
- Lightweight construction – reduces energy consumption in transportation.
- Corrosion resistance – ideal for outdoor and marine environments.
- Dimensional precision – supports tight tolerances in complex assemblies.
- High recyclability – aluminum can be reused repeatedly without degradation.
Whether for high-volume automotive parts or low-volume industrial prototypes, aluminum casting delivers exceptional value across the product lifecycle.
🛠️ Key Aluminum Casting Processes (Comparison Table)
| Process | Description | Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | High-pressure injection into steel molds | Excellent surface finish, fast production | Engine housings, electronic enclosures |
| Sand Casting | Molten metal poured into sand molds | Low cost, suitable for large parts | Pump housings, brackets |
| Permanent Mold | Uses reusable metal molds (without pressure) | Stronger than sand casting, good repeatability | Wheels, suspension components |
| Investment Casting | Wax pattern and ceramic mold for intricate shapes | High accuracy, thin walls | Aerospace parts, medical devices |
Each casting method offers trade-offs in cost, complexity, and performance. Choosing the right process depends on production scale and part requirements.
⚙️ Mechanical Properties of Aluminum Castings
Aluminum castings are valued for a unique combination of lightweight structure and mechanical durability.
| Property | Performance Notes |
|---|---|
| Density | ~2.7 g/cm³ (about 1/3 of steel or iron) |
| Tensile Strength | Varies by alloy and process (e.g., up to 350 MPa for die cast parts) |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent for heat dissipation (150–200 W/m·K) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance in atmospheric and marine environments |
| Machinability | Good, especially for die cast or permanent mold parts |
These properties make aluminum casting a top choice for engineers targeting lightweight yet functional components.
🏭 Applications of Aluminum Castings
Aluminum castings are widely used across multiple sectors due to their light weight, corrosion resistance, and cost-efficiency:
- Automotive: Engine blocks, cylinder heads, transmission housings, suspension arms
- Aerospace: Brackets, casings, interior structural supports
- Industrial Equipment: Gear housings, robotic parts, compressor shells
- Electronics: Heat sinks, LED housings, enclosures
- Infrastructure: Lighting fixtures, mounting arms, support brackets
Their adaptability makes them suitable for both precision components and large-volume production.
Common aluminum casting applications across key industries.
🧪 Aluminum vs. Other Casting Materials
| Feature | Aluminum Casting | Cast Iron | Cast Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | ⭐ Very Light | ❌ Heavy | ❌ Heavy |
| Strength | ✅ Moderate–High | ✅ High (brittle) | ✅ High (ductile) |
| Corrosion Resistance | ✅ Excellent | ❌ Poor | ✅ Moderate |
| Machinability | ✅ Good | ❌ Moderate | ❌ Harder to machine |
| Cost | ✅ Moderate | ✅ Low | ❌ Higher |
| Recyclability | ✅ Very High | ✅ High | ✅ High |
✅ = favorable trait, ❌ = less favorable, ⭐ = best-in-class
Aluminum stands out where lightweighting, corrosion resistance, and manufacturability are key—especially in transportation and electronics.
Common Aluminum Alloys Used in Casting
Different casting alloys offer varying properties that influence strength, machinability, and corrosion resistance.
| Alloy | Key Features | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| ADC12 | Excellent castability, moderate strength | Die-cast engine parts, housings |
| A356 | High strength and ductility, weldable | Sand-cast wheels, suspension arms |
| A319 | Good thermal resistance and corrosion protection | Cylinder heads, compressor parts |
| A380 | Dimensional stability, good flow | Electronic housings, appliance parts |
Choosing the right alloy ensures performance targets are met without overengineering the part.
How to Choose the Right Aluminum Casting Process
Selecting the ideal aluminum casting process depends on various factors:
- Production Volume: High-volume products benefit from die casting; low-to-medium fits sand or permanent mold.
- Part Complexity: Intricate geometries may require investment casting.
- Mechanical Requirements: Consider strength, heat resistance, and tolerances.
- Cost Constraints: Sand casting is more affordable for prototypes; die casting is efficient at scale.
Consulting a casting expert helps match the process to your design, budget, and timeline.
✅ Conclusion
Aluminum casting is a highly adaptable manufacturing process that delivers lightweight, strong, and corrosion-resistant components across critical industries. By selecting the right casting method and alloy, manufacturers can meet demanding performance, design, and sustainability goals.
If you’re seeking reliable aluminum casting solutions for industrial or commercial applications, understanding the available processes and their benefits is key to making an informed choice.
📩 Get Expert Support
Looking for a trusted aluminum casting partner?
👉 Contact us to discuss your custom casting requirements.
We provide sand casting, die casting, and precision aluminum components tailored to your specifications.






