What is Bronze: Definition, Types, Applications
Bronze is a copper-based alloy, primarily with tin as its core element. This precise ratio…
We supply a full range of brass casting alloys to support sand casting and gravity casting for industrial applications.


| Alloy Grade | Key Properties | Typical Applications | Example Parts |
|---|---|---|---|
| HPb59-1 (C37700) | High-strength forging brass with very good hot workability, dense structure after forging or casting, and good machinability for sealing and threaded surfaces. | Plumbing and HVAC valves and fittings, gas and water control components, pump and compressor parts. | Forged Valve Body, Angle Valve, Pump Housing |
| HPb63-3 (C36000) | Free-cutting brass with excellent machinability and chip breaking; ideal for high-speed turning of precision brass components. | Hydraulic and pneumatic connectors, precision threaded inserts, small valve and instrument components. | Threaded Insert, Hose Fitting, Valve Spool |
| HPb61-1 | Medium-strength leaded brass with good machinability, adequate corrosion resistance, and stable dimensional accuracy after machining. | Hydraulic adaptors, machined bushings, medium-pressure fluid control components. | Bushing, Sleeve, Valve Plug |
| H62 (C28000) | Medium-strength brass with balanced toughness and castability; good wear resistance and suitable for subsequent machining. | Structural brass parts in plumbing, pump and valve assemblies, and light mechanical components. | Valve Seat, Connector Body, Support Bracket |
| H59 | Strong and economical structural brass, suitable for hot working and machining of robust hardware and fittings. | Machinery components, plumbing hardware, flanges and brackets for general engineering. | Nut, Insert, Flange Connector |
| H65 (C27000) | Medium-strength brass with good cold and hot workability, offering reliable machinability for precision components. | Mechanical fittings, watch and instrument components, small housings and connectors. | Bushing, Precision Ring, Connector Shell |
| H68 (C26800) | Good strength-to-ductility ratio and stable forming behaviour; suitable for profiles requiring both rigidity and bendability. | Connector bodies, decorative and architectural hardware, general brass structural parts. | Connector Clip, Nameplate, Mounting Bracket |
| H63 (C27200) | Versatile brass grade with excellent formability and moderate strength; suitable for parts that require secondary machining. | Automotive and electrical hardware, sleeves and shells, medium-precision components. | Connector Shell, Spacer Tube, Ferrule |
| H70 (C26000) | High-ductility brass with excellent cold-forming performance and good bending properties. | Contact components, flexible connector parts, precision shims and spring-like brass elements. | Contact Terminal, Precision Shim, Thin Connector Strip |
| H85 (C23000) | Brass with relatively high copper content, offering good corrosion resistance and formability with moderate strength. | Architectural and decorative hardware, industrial fittings, instrument enclosures. | Valve Cover, Decorative Trim, Instrument Housing |
| H90 (C22000) | High-copper brass with good ductility and corrosion resistance; suitable for shaped profiles and functional contact parts. | Electrical and electronic hardware, lighting components, precision contact parts. | Contact Lug, Connector Ring, Hardware Sleeve |
| H96 (C21000) | Very high copper content with excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, and good resistance to atmospheric corrosion. | Electrical connection components, busbars, heat-transfer and grounding parts. | Earthing Bar, Connector Bus, Heat Transfer Plate |
| Capability | Minhe Brass Casting |
|---|---|
| Maximum casting size |
Typically up to 250 × 120 × 150 mm for brass castings; larger components can be evaluated based on geometry and tooling. |
| Weight range | Approx. 0.2 – 30 kg per part depending on process (sand casting / gravity casting). |
| Minimum wall thickness |
Brass gravity casting typically supports 2.5–4.0 mm walls; sand casting usually requires 4–6 mm. |
| Dimensional tolerance |
As-cast accuracy around ISO 8062-3 CT7–CT9 for brass alloys; CNC machining enables precision features down to ±0.10–0.15 mm. |
| Surface roughness (as-cast) |
Brass castings typically achieve Ra 6.3–25 μm as-cast; machined surfaces can reach Ra 1.6–3.2 μm. |
| Typical lead time |
Samples usually ready in 10–12 days after tool approval; mass production typically 3–4 weeks. |
| Annual brass casting capacity | Combined brass casting capacity of approx. 1,800 tons / year. |
| Processes supported |
Sand casting, gravity casting, heat treatment & full in-house CNC machining. |
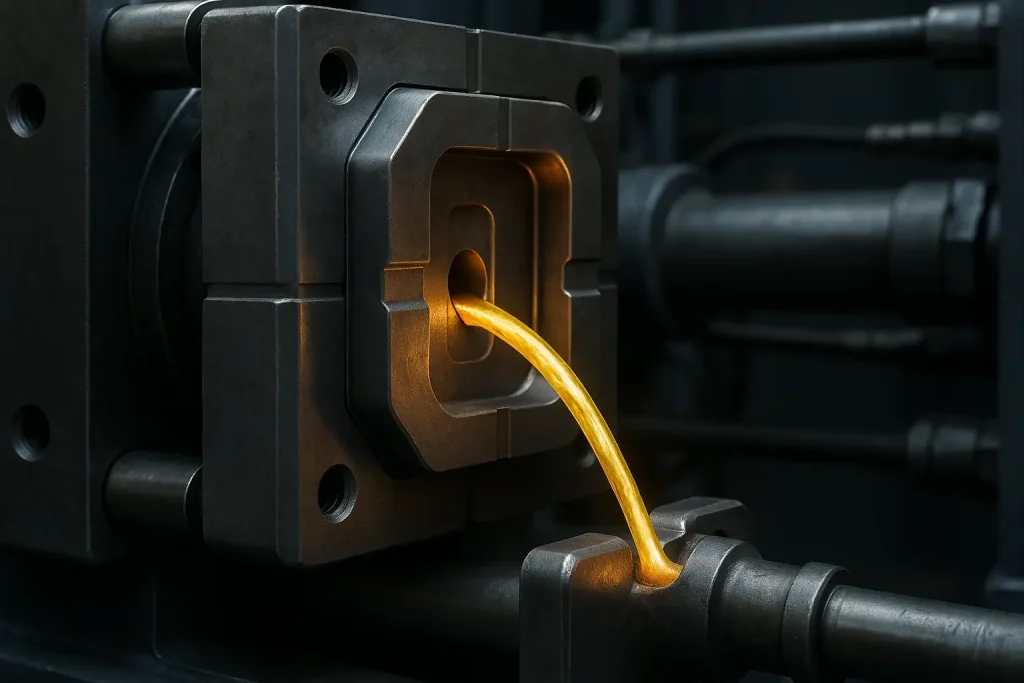
Die casting enables the production of thin-wall and complex geometries under high pressure, delivering exceptional dimensional accuracy and consistency.
It is ideal for high-volume manufacturing of precision metal components with strict tolerance requirements.

Gravity casting uses reusable metal molds and gravity-fed pouring to achieve improved density and stable dimensions.
This process suits medium- to large-sized structural parts, offering reduced internal defects and lower tooling costs than high-pressure die casting.
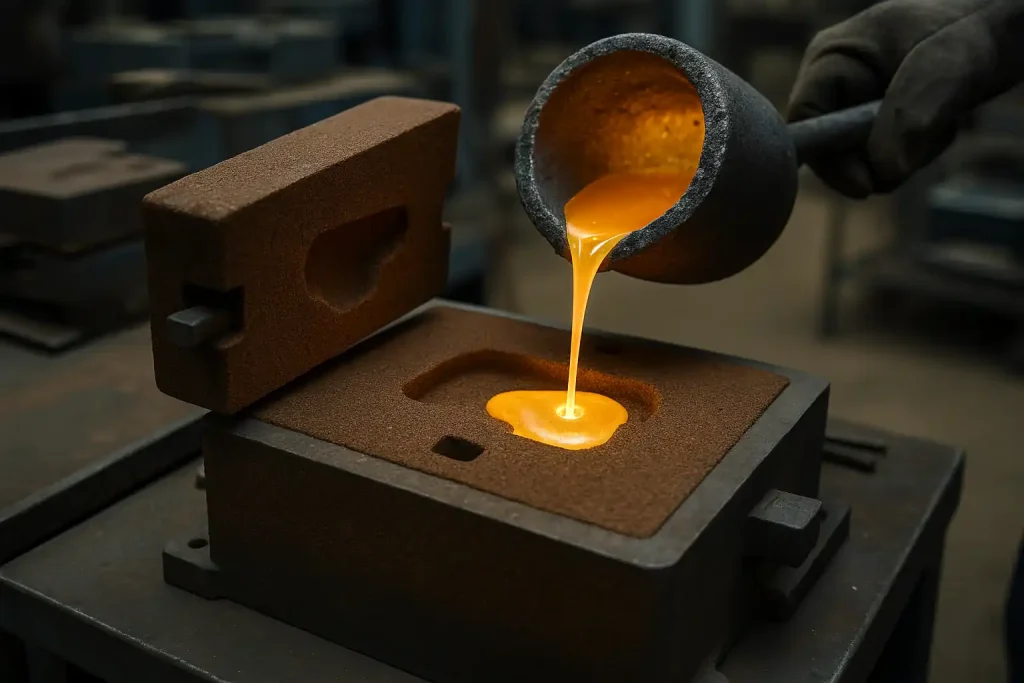

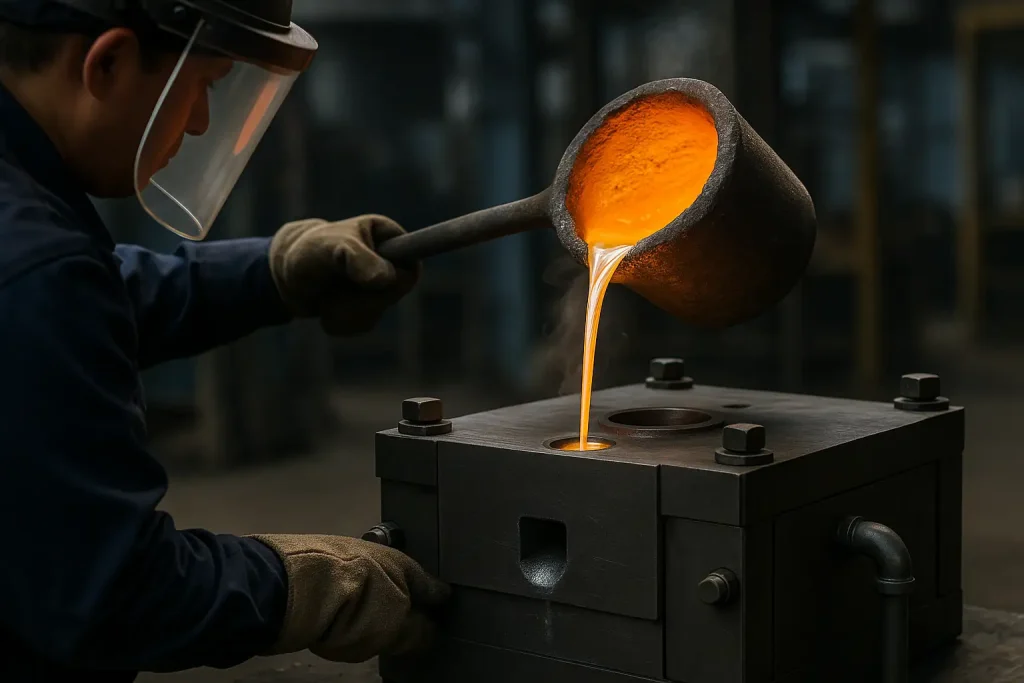
Sand casting forms parts by pouring molten metal into expendable sand molds, allowing greater freedom in shape and section thickness.
It is suitable for prototypes, low-volume production, and large structural components where cost efficiency and flexible design are priorities.
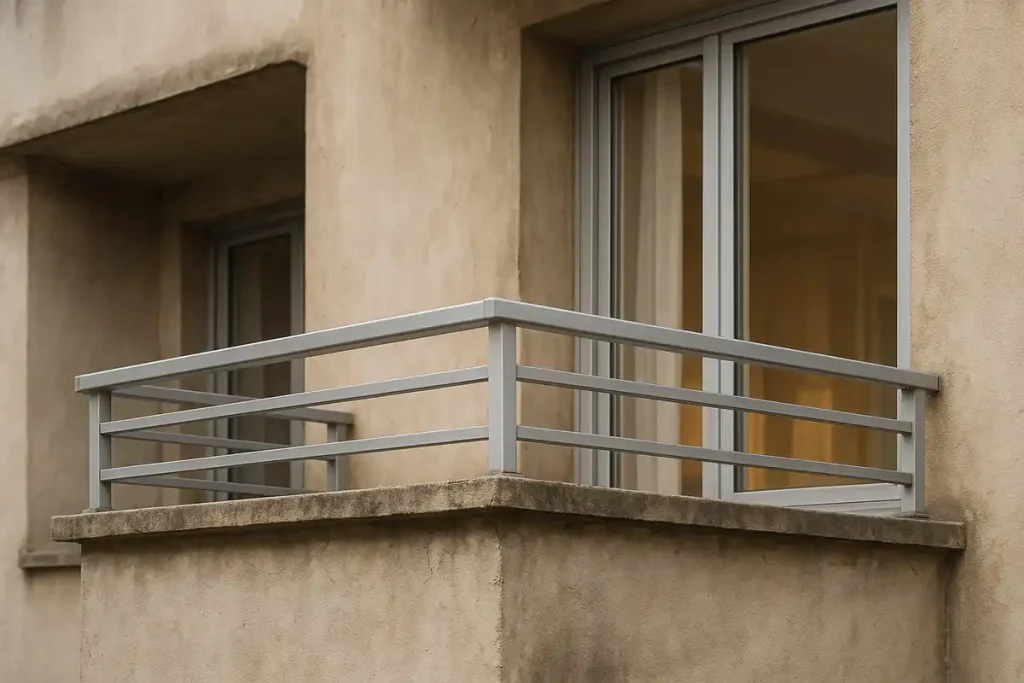

Brass is widely used in door locks, hinges, railings, decorative trims, and window/door hardware, providing both mechanical durability and premium aesthetic appeal.
Its natural corrosion resistance supports long service life in outdoor architectural environments.
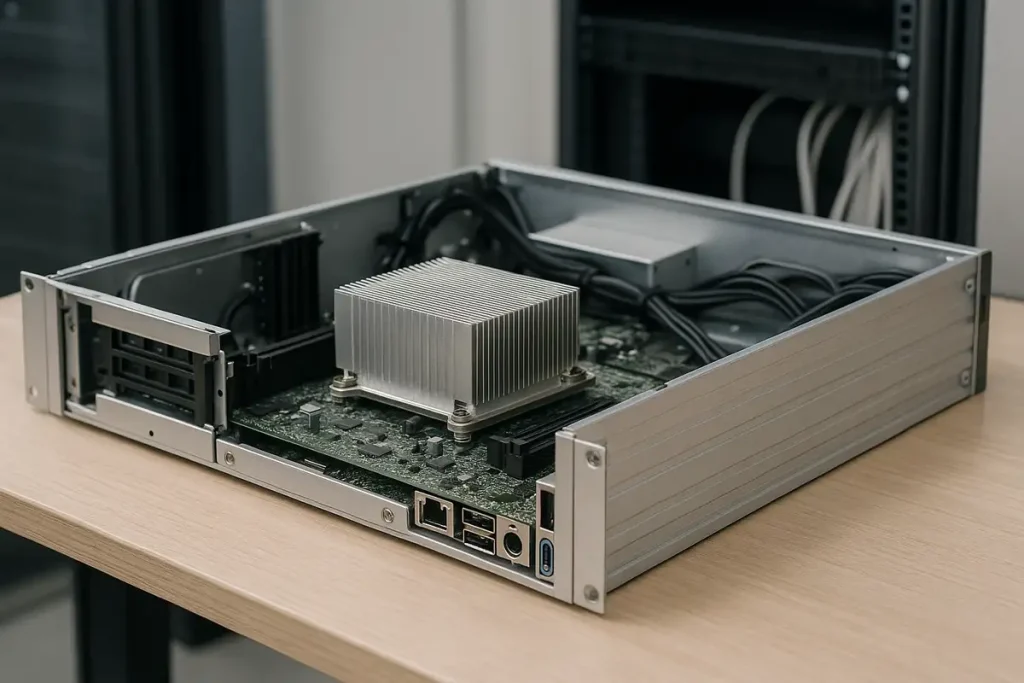

Brass offers excellent electrical conductivity, dimensional stability, and anti-sparking performance, making it ideal for bus bars, grounding terminals, connectors, and switchgear parts.
It ensures reliable power transfer in consumer electronics, industrial control systems, and high-voltage equipment.
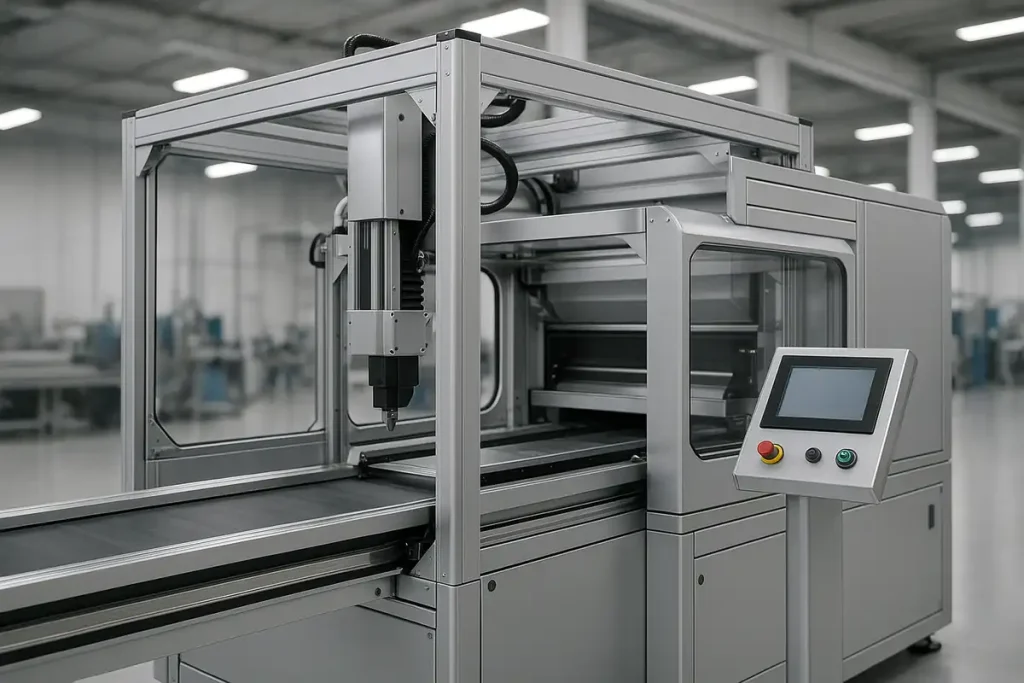

Brass is preferred for pump bodies, valve seats, precision fittings, and threaded connectors, due to its stable machinability and resistance to corrosion in water, oils, and non-aggressive chemicals.
Common applications include hydraulic valve assemblies, plumbing fittings, compressor components, and gas or water control systems.
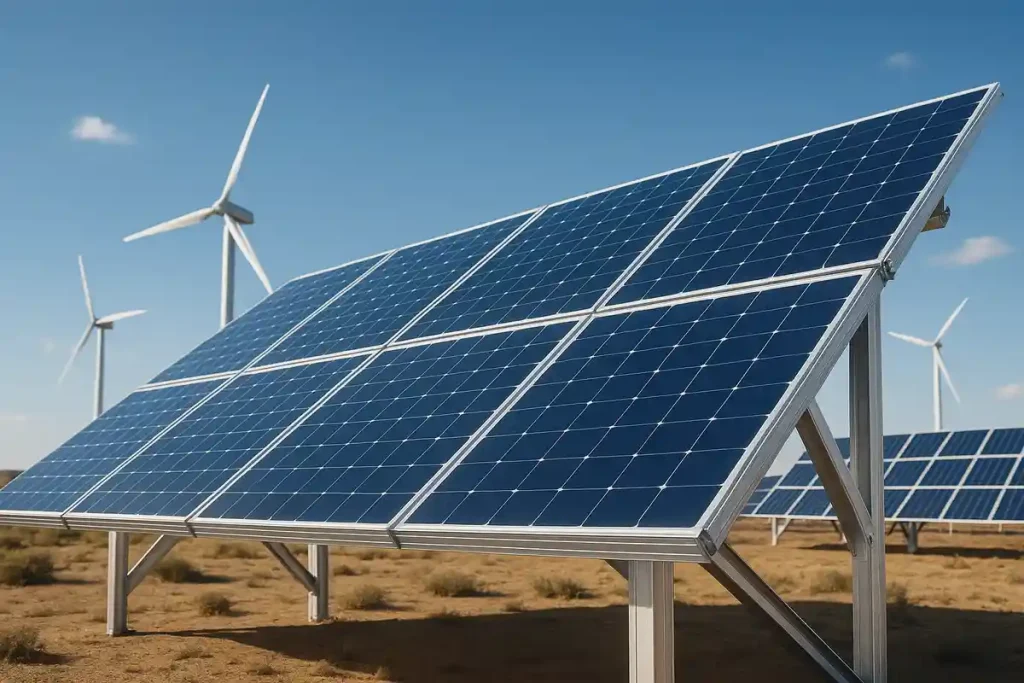

Crucial for renewable and traditional power systems, primarily due to its light weight and resistance to weathering. Applications include solar panel mounting frames, wind turbine components, and high-voltage transmission lines.

Due to its premium finish, durability, and friction resistance, brass is commonly used in faucets, sanitary fittings, luxury hardware, musical instruments, zippers, and precision hand tools.
It combines aesthetics with reliable wear performance.
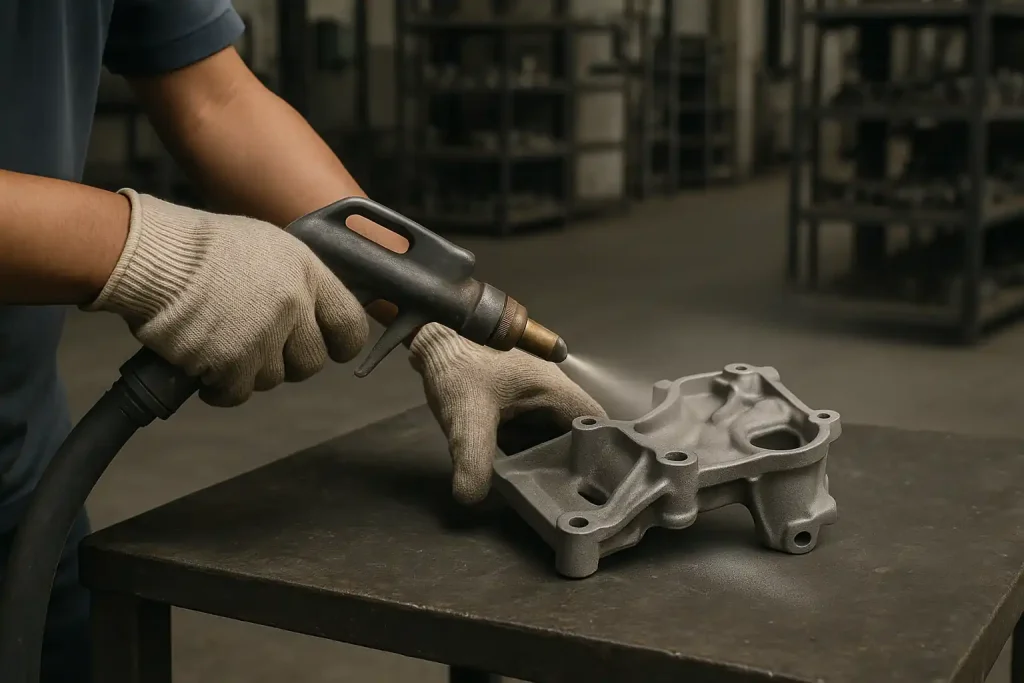

Removes casting flash, sand residues, and oxide layers through trimming, deburring, shot blasting, and high-pressure cleaning, creating a clean and uniform surface for the next processing stages.
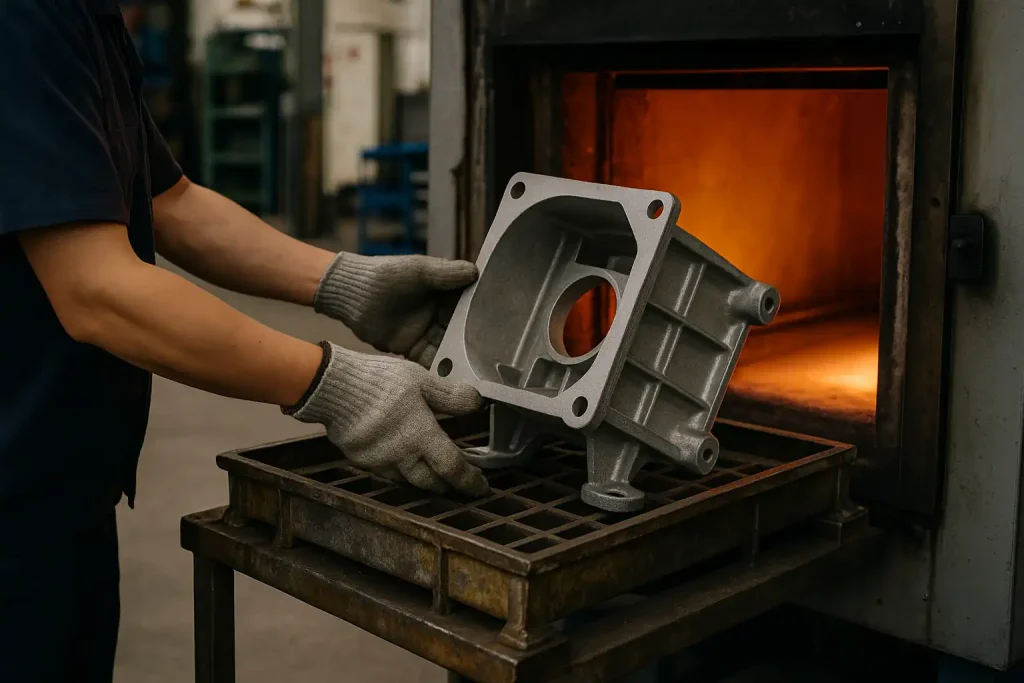

Enhances strength and dimensional stability by applying annealing, normalizing, quenching, tempering, or solution-aging treatments, depending on alloy type and performance requirements of the casting.
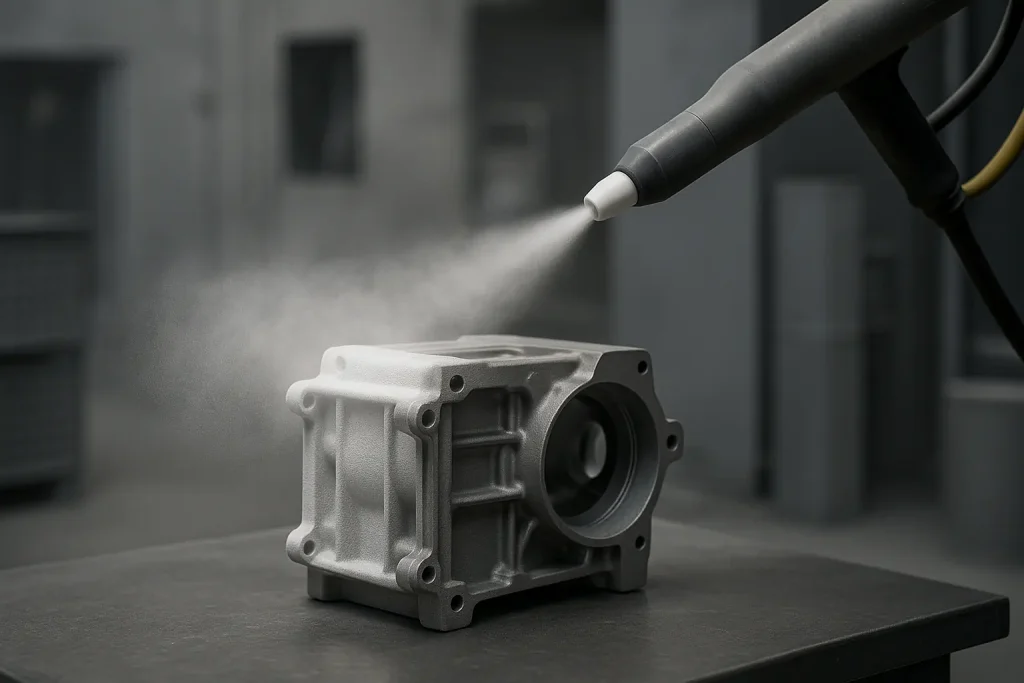

Improves corrosion resistance, wear protection, and final appearance through anodizing, painting, powder coating, or e-coating. These finishes provide durable, application-specific protection for aluminum castings.
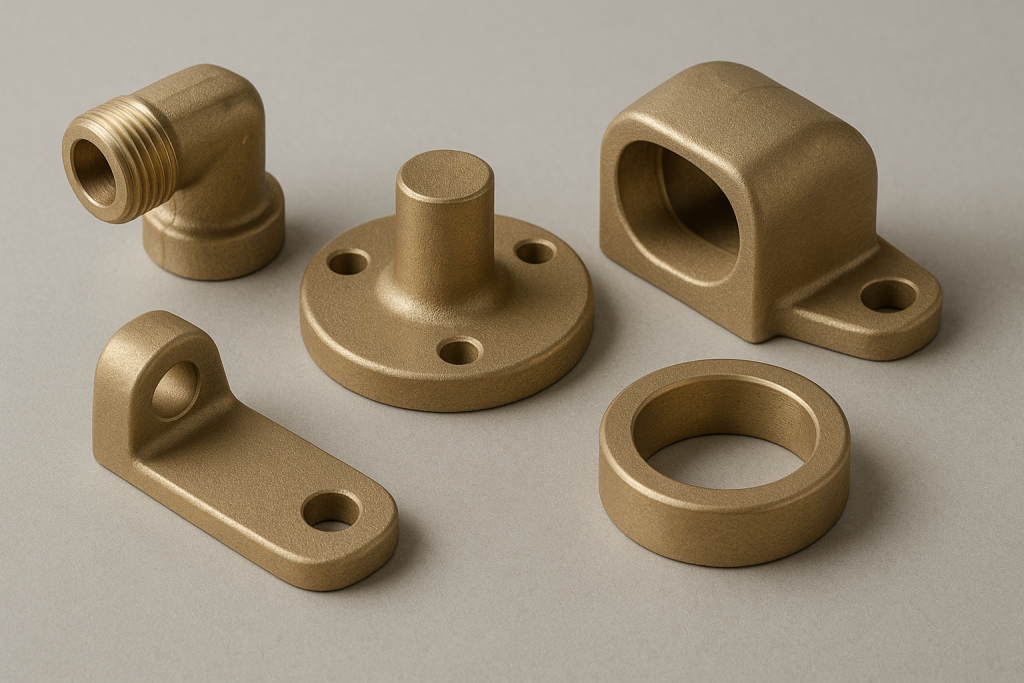
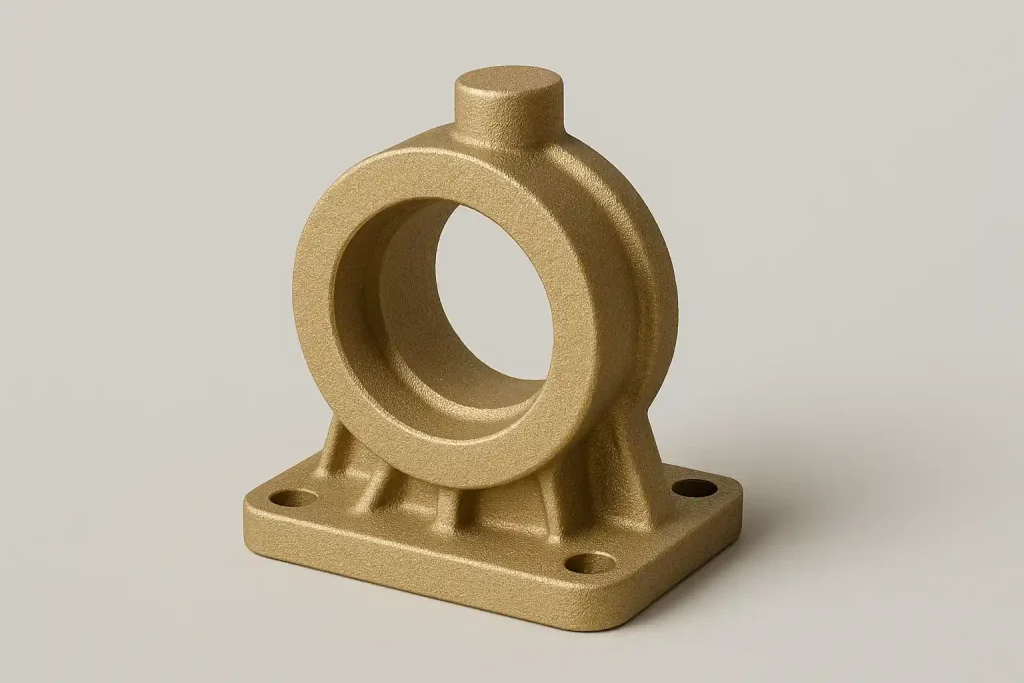


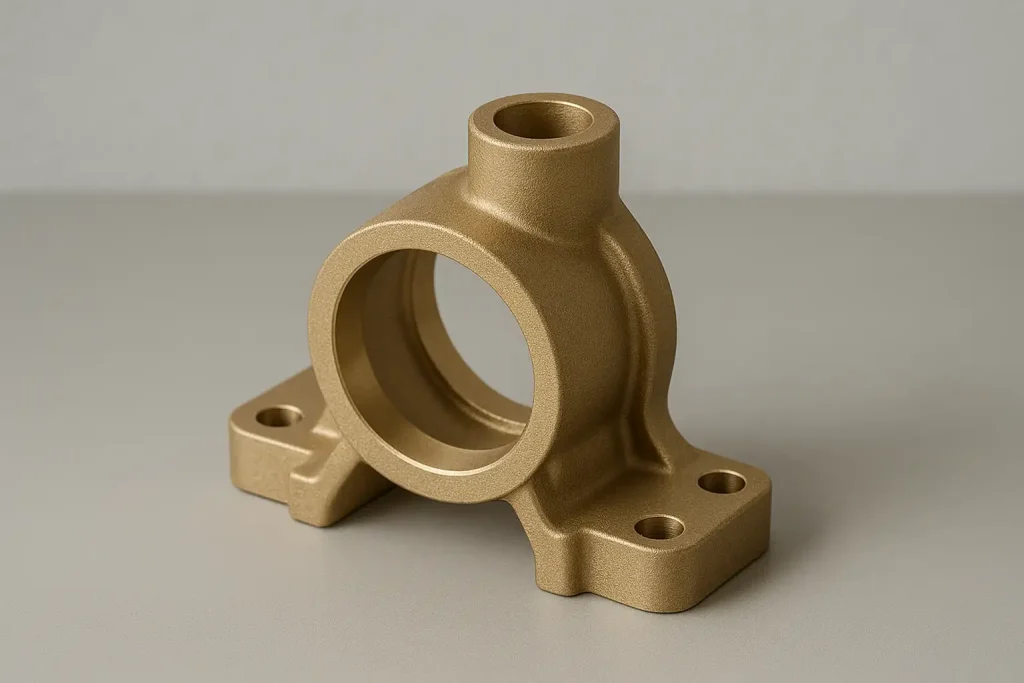
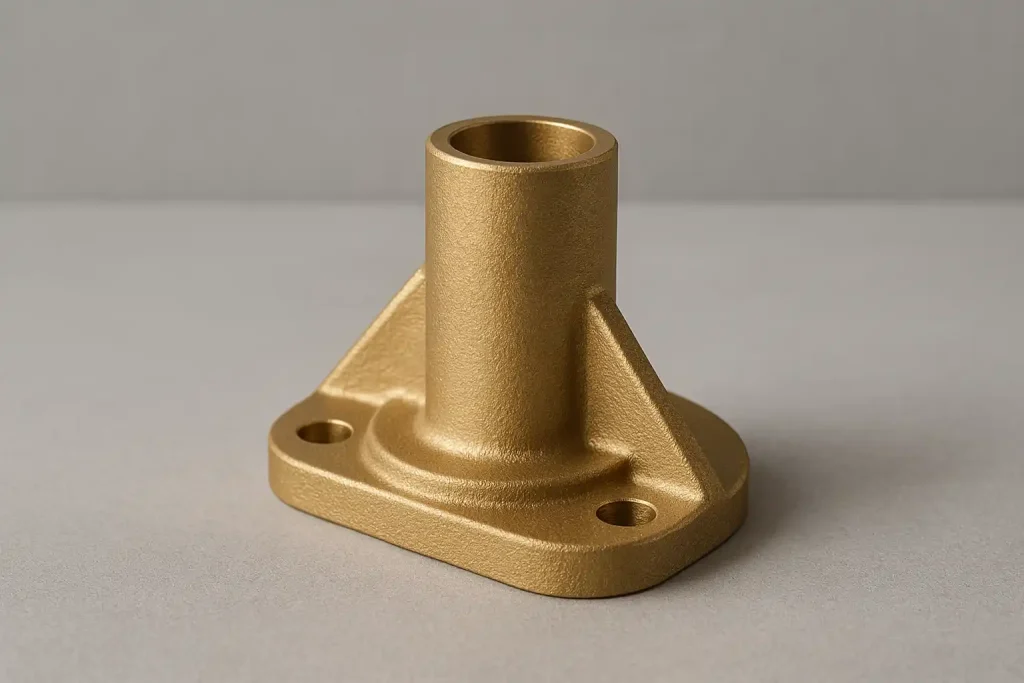
Brass Housing
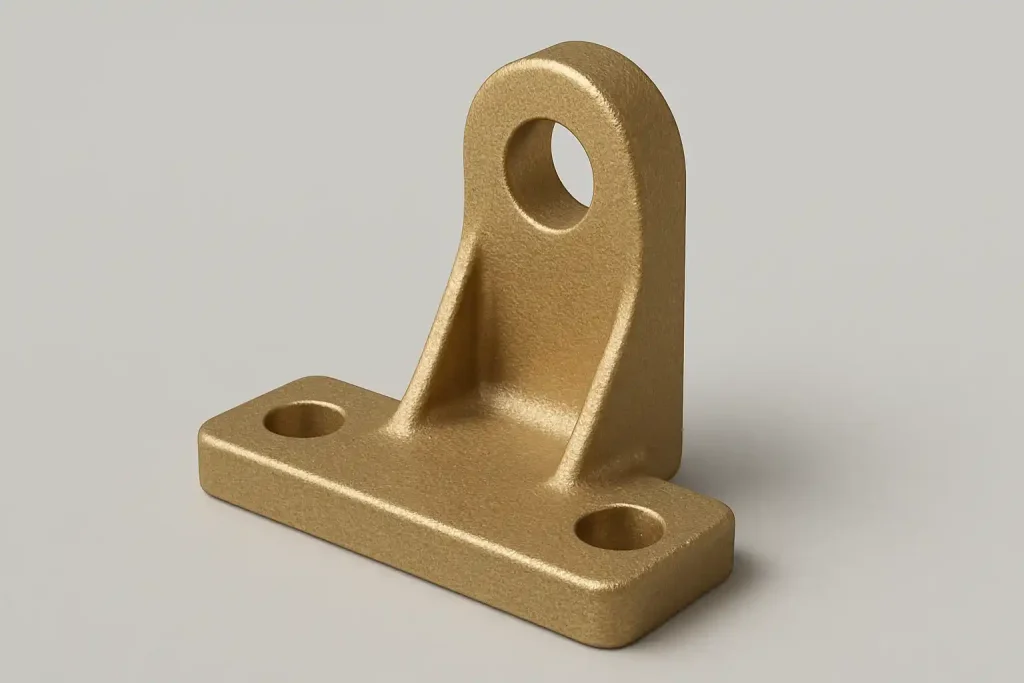

Brass Bracket
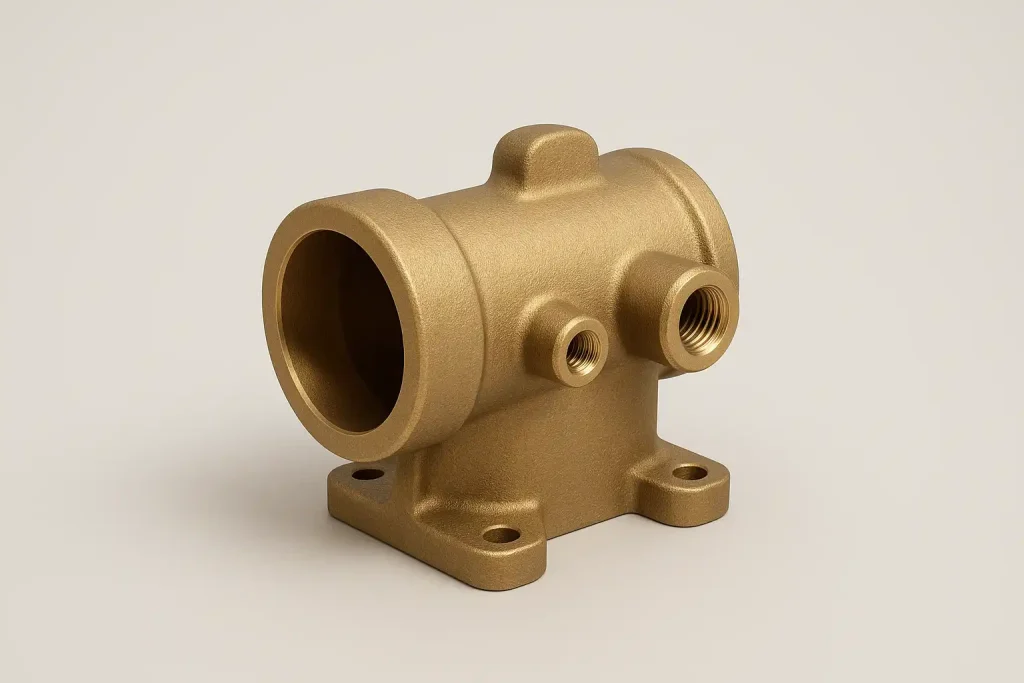

Brass Pump Body
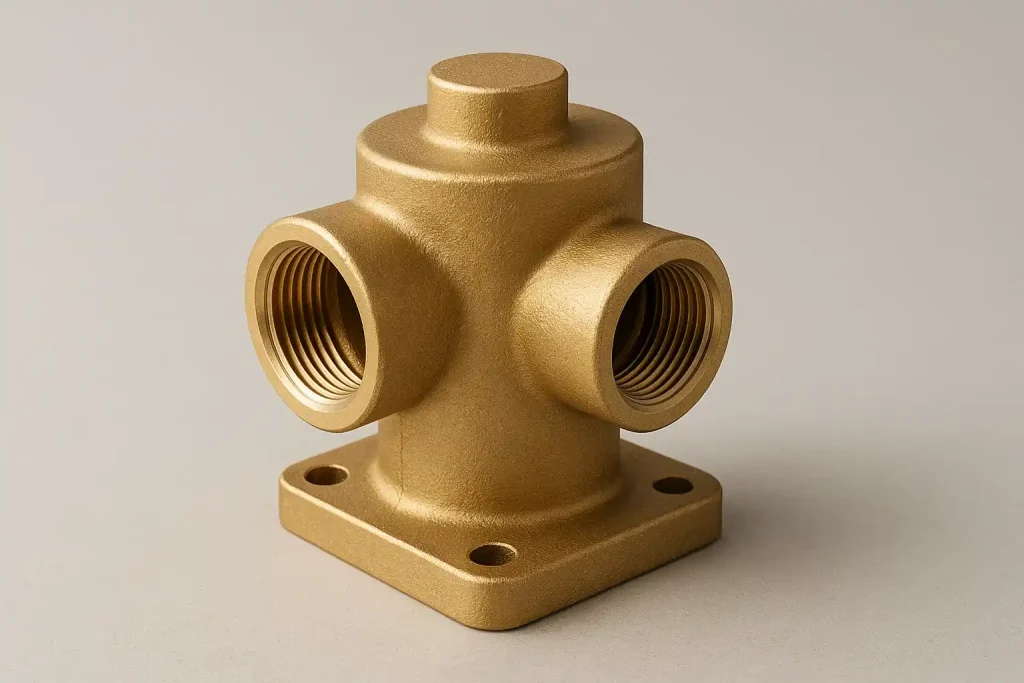

Brass Valve Body
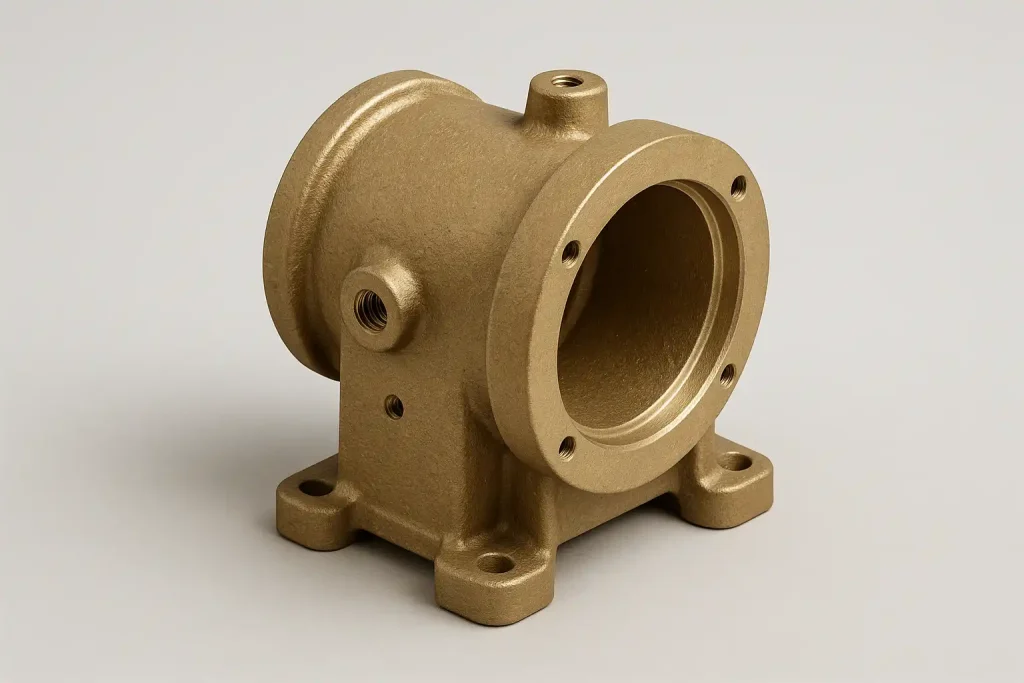

Brass Gearbox Case
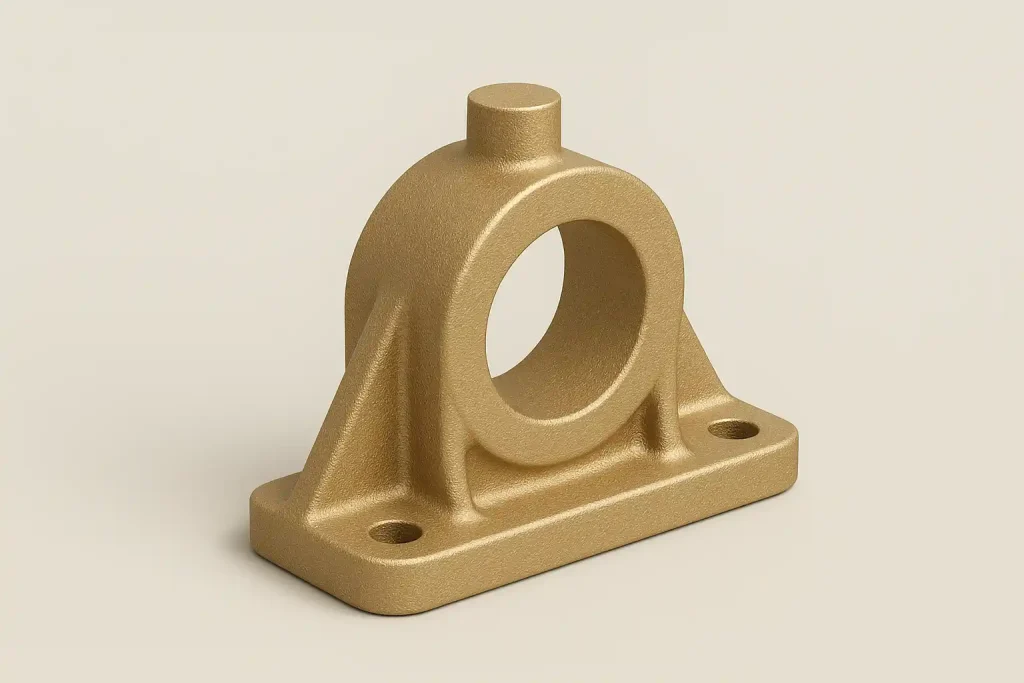

Brass Structural Part
Bronze is a copper-based alloy, primarily with tin as its core element. This precise ratio…
Bronze and brass are two common copper alloys, but they have significant differences in composition,…
Gray cast iron is an iron-carbon alloy named for its gray fracture surface. The article…